
The quality of an education system to a greater extent depends on the standard of its assessment practices. When the standards of assessments are poised at a higher level of learning, then obviously the curriculum and the learning experience should keep in pace with the level of evaluation standards. Hence it is truly said that assessment is an engine that drives the students’ learning.
One of the common recommendations by several committees on examination reform do insist that the Higher order thinking skills of the scholars need to be tested especially at higher education level. In this context it seems more relevant to conduct a study on to what extent the Indian University and Higher Education systems endorse this policy.
St. Philomena’s (Autonomous) College, Mysore in collaboration with ipsr solutions limited had conducted a National Level FDP program on Outcome Based Education. More than 1000 teachers participated from almost all states of India. One of the sessions was on Bloom’s Taxonomy and the teachers have submitted an activity named – Question paper analysis intended to analyze one of the previous year’s University question papers in their subject in line with the cognitive domain of Bloom’s Taxonomy.
A sample of 220 reports of analysis from various teachers of different states were randomly selected and analysed. The major observation of the Analysis is given below:
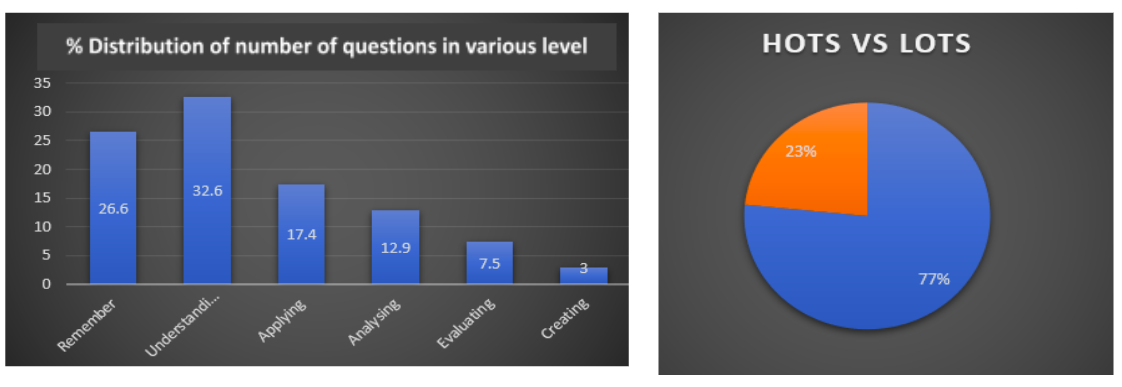
1. It is observed that an average of 77% of the questions are from Lower Order Thinking Skills (LOTS). While the Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) like Analytical, Evaluation type and creating type questions are much less.
2. It is further observed that when considering the average number of questions from various level of bloom’s taxonomy maximum number of questions are from conceptual level and remembering level, that is 59.2% of the questions are direct and of very lower order as per Bloom’s Taxonomy.
3. It is found that 30.3% of the questions on an average is testing the student’s learning in application of the concepts in relevant situations and their ability to analyze a situation and identify the relationship between various components involved in the situation.
4. It is also observed that an average of 3% questions are from create level which are normally from arts related discipline.
5. Considering the average weightage of marks related to various levels of learning it is observed that 69% of marks are related to Lower Order Thinking skill (LOTS) questions.
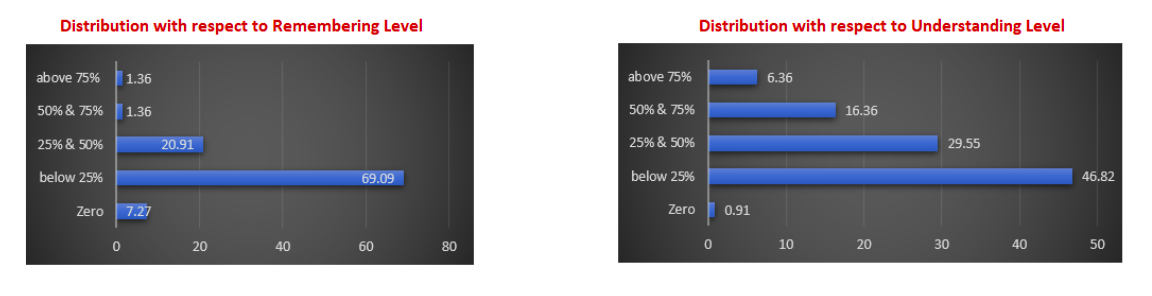
7. It is noted that 7.27% of questions papers analysed do not have any question from remembering level. 69.09% of the question paper has less than 25% questions from the remembering level.
8. 22.7 % of the question paper is having more than 50% of questions from understanding level, while 46.82% of the question paper is having less than 25% of questions from understanding level. Also less than 1% of the question paper is not having any questions from understanding level.
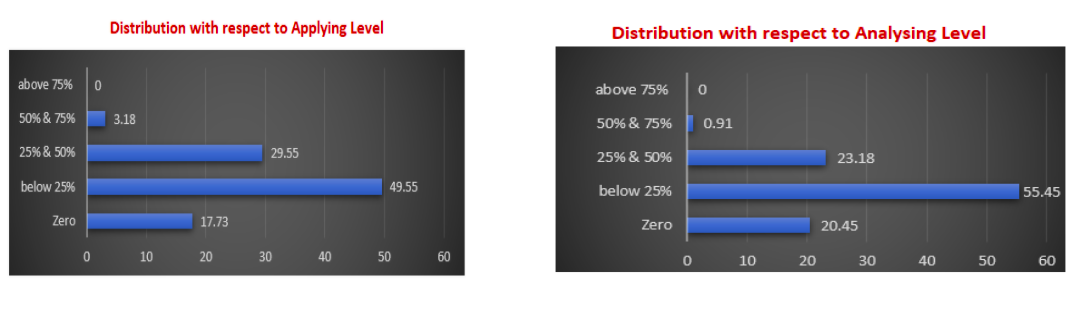
9. 17.73% of the question papers do not have any questions from application level and 20.45% of question papers do not have any questions from analytical level.
10. Only 3.18% percent of the question paper is having more than 50% of questions from application level and less than 1% of the question paper is having more than 50% of analytical level questions.
11. 79.1% of question papers have only less than 25% of questions from application level and 78.63% of question papers have only less than 25% of analytical level questions.
12. 42.73% of question papers do not have any questions from evaluation level and 67.73% of question paper do not have any create level questions
13. It is also noted that 0.91% of question papers are having create level questions in a range of 25% to 50%.
Join us for FREE to get instant email updates!

Assumption College, Changanacherry adopts QnSmart Question Bank System to improve question paper quality.
Mahatma Gandhi University, Kerala has implemented QnSmart Question Bank System, to achieve great efficiency and reduced cost, within the initial months itself.
Very good informative research findings