Outcome-Based Education (OBE) has emerged as a transformative approach in the contemporary educational landscape, emphasizing the significance of clearly defined learning outcomes. By centring the educational process around specific skills and competencies students are expected to acquire, OBE fosters a more engaging and accountable learning environment. This paradigm shift not only enhances student engagement but also ensures that educational institutions are aligned with the needs of employers and society at large.
Incorporating generative AI into teaching and learning amplifies the effectiveness of OBE. Generative AI tools can assist educators in developing personalized learning experiences tailored to individual student needs. By analyzing student data and behaviour, these tools provide insights that allow for the creation of adaptive learning paths, thereby enhancing the overall learning experience and supporting diverse learning styles.
Furthermore, generative AI facilitates the creation of dynamic and interactive learning materials, making education more accessible and engaging. From generating quizzes and assignments to developing simulations and visual aids, AI technology enables educators to focus on higher-order teaching strategies while automating routine tasks. This integration of technology not only enhances instructional quality but also prepares students for a future where digital literacy is paramount.
The combination of OBE and generative AI is particularly significant in promoting lifelong learning. As the job market continually evolves, students must develop a mindset of continuous improvement and adaptability. Generative AI can play a critical role in this by offering real-time feedback and resources that empower students to take control of their learning journey, thereby fostering independence and critical thinking skills.
Moreover, the collaborative potential of generative AI encourages teamwork and communication among students. By utilizing AI-driven platforms, students can engage in collaborative projects that reflect real-world scenarios, promoting skills that are essential in today’s interconnected workforce. This collaborative learning environment nurtures creativity and innovation, vital competencies for future success.
As educational institutions increasingly embrace OBE and generative AI, it is essential to address the challenges that accompany these changes. Educators must be equipped with the necessary training and resources to effectively integrate these methodologies into their teaching practices. Additionally, considerations regarding data privacy and the ethical implications of AI use in education must be paramount to ensure a responsible and equitable approach.
In conclusion, the integration of Outcome-Based Education and generative AI represents a significant advancement in the educational system. By focusing on clearly defined outcomes and leveraging cutting-edge technology, educators can create a more personalized, engaging, and effective learning experience. This synergy not only prepares students for the challenges of the future but also enhances the overall quality and relevance of education in an ever-changing world.
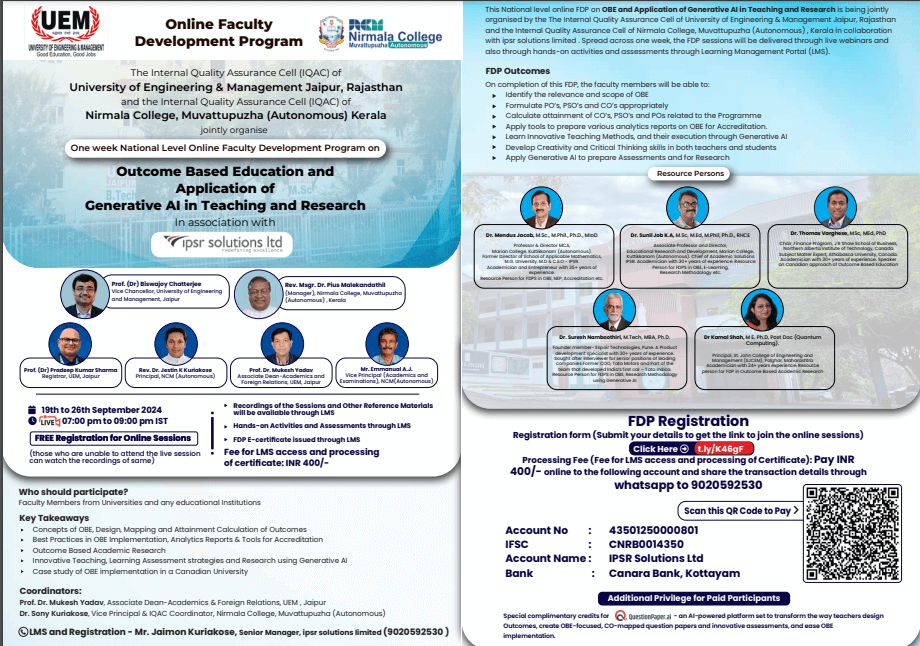
Participants in the Faculty Development Programme include Deans, Heads of Departments, and Faculty Members from Higher Educational Institutions across the Indian States and abroad.
2287 participants took part and benefitted from the seven-day Faculty Development Programme on Outcome Based Education and Application of Generative AI in Teaching and Research organised by the Internal Quality Assurance Cells of the University of Engineering and Management, Jaipur, Rajasthan and Nirmala College, Muvattupuzha, Autonomous in association with ipsr solutions limited.
Day 1 Technical Session:
Topic: Bloom’s Taxonomy – Learning Domains by Dr Sunil Job KA.
Dr Sunil Job, the resource person on the first day’s session handled the topic Bloom’s Taxonomy – Learning Domains.
 Bloom’s Taxonomy is a framework that categorizes learning objectives into distinct domains, helping educators design and assess educational experiences. Originally developed by Benjamin Bloom in 1956, the taxonomy consists of three primary domains: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. The cognitive domain focuses on mental skills and knowledge acquisition, the affective domain addresses emotional aspects and attitudes, and the psychomotor domain pertains to physical skills and coordination.
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a framework that categorizes learning objectives into distinct domains, helping educators design and assess educational experiences. Originally developed by Benjamin Bloom in 1956, the taxonomy consists of three primary domains: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. The cognitive domain focuses on mental skills and knowledge acquisition, the affective domain addresses emotional aspects and attitudes, and the psychomotor domain pertains to physical skills and coordination.
The cognitive domain focuses on mental skills and knowledge acquisition, encompassing levels from basic recall of facts to higher-order thinking skills like analysis and evaluation. The affective domain addresses emotions, attitudes, and values, emphasizing the importance of personal growth and emotional development in the learning process. Lastly, the psychomotor domain involves physical skills and coordination, highlighting the role of hands-on experiences in learning. Together, these domains create a holistic framework that supports diverse learning experiences and outcomes.
Understanding these domains allows educators to create well-rounded curricula that engage students on multiple levels, fostering not only intellectual growth but also emotional intelligence and practical skills. By leveraging Bloom’s Taxonomy, educators can enhance learning outcomes and promote deeper understanding across various disciplines.
The first task, Question Paper Analysis based on Bloom’s Taxonomy was assigned to the participants at the end of the first day’s session Bloom’s Taxonomy, Learning Domains by Dr Sunil Job.
Click to watch the video recording of the first day’s session, Blooms Taxonomy – Learning Domains by Dr Sunil Job.
Day 2 Technical Session:
Topic: Architecture of OBE & Design of Outcomes by Dr Sunil Job KA.
Dr Sunil Job was the resource person on the second day and the topic for the session was Architecture of OBE & Design of Outcomes.
 The architecture of Outcome-Based Education (OBE) is centred on defining clear, measurable outcomes that students are expected to achieve by the end of an educational program. This approach emphasizes the importance of what learners should be able to demonstrate upon completion of a course or program, ensuring that all educational activities align with defined learning outcomes. By establishing specific, measurable outcomes, OBE provides a structured pathway for both educators and students to assess and enhance learning effectiveness.
The architecture of Outcome-Based Education (OBE) is centred on defining clear, measurable outcomes that students are expected to achieve by the end of an educational program. This approach emphasizes the importance of what learners should be able to demonstrate upon completion of a course or program, ensuring that all educational activities align with defined learning outcomes. By establishing specific, measurable outcomes, OBE provides a structured pathway for both educators and students to assess and enhance learning effectiveness.
In the design of outcomes within OBE, careful consideration is given to the needs of various stakeholders, including students, employers, and the community. This involves developing outcomes that not only reflect academic proficiency but also encompass critical thinking, problem-solving, and practical application of knowledge. By fostering a learner-centred environment, OBE promotes continuous improvement in educational practices, ensuring that graduates are well-prepared to meet the demands of an ever-evolving workforce.
Ultimately, the architecture of OBE and the thoughtful design of outcomes promote a learner-centred environment that encourages active participation and continuous improvement. By prioritizing measurable achievements, educational institutions can foster accountability, transparency, and a commitment to quality in teaching and learning. This approach not only enhances student engagement but also ensures that graduates are well-equipped with the skills and knowledge necessary for success in their chosen fields.
The second task, Workshop Activity – Course Outcome and Quality Check was assigned to the participants after the second day’s session, Architecture of OBE, Designs of Outcomes by Dr Sunil Job.
Click to watch the video recording of the second day’s session, Architecture of OBE & Design of Outcomes by Dr Sunil Job.
Day 3 Technical Session:
Topic: Architecture of OBE & Design of Outcomes by Dr Sunil Job KA.
Dr Thomas Varghese was the resource person for the third day of the one-week Faculty Development Programme Outcome Based Education and Application of Generative AI in Teaching and Research, with the topic Outcome Based Education – A Canadian Experience.
 Outcome-Based Education (OBE) is a pedagogical approach that emphasizes clearly defined learning outcomes as the foundation for curriculum design and assessment. In Canada, OBE has gained traction as an effective method to enhance student engagement and achievement. By focusing on the specific skills and competencies that students should acquire by the end of a course or program, educators can create a more personalized and relevant learning experience that caters to diverse student needs.
Outcome-Based Education (OBE) is a pedagogical approach that emphasizes clearly defined learning outcomes as the foundation for curriculum design and assessment. In Canada, OBE has gained traction as an effective method to enhance student engagement and achievement. By focusing on the specific skills and competencies that students should acquire by the end of a course or program, educators can create a more personalized and relevant learning experience that caters to diverse student needs.
The Canadian experience with OBE reflects a commitment to educational reform aimed at improving the quality of learning. Various provinces have adopted OBE principles in their K-12 and post-secondary systems, leading to the development of innovative curricula that prioritize critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaborative skills. This shift is not only about the content delivered but also about how students demonstrate their understanding and application of knowledge in real-world contexts.
Moreover, OBE in Canada promotes a culture of continuous improvement and accountability among educators. By utilizing assessment tools that align with defined outcomes, institutions can track student progress and refine teaching strategies accordingly. This evidence-based approach fosters a learning environment that encourages student autonomy and fosters lifelong learning, ultimately preparing graduates to thrive in a rapidly changing global landscape.
Click to watch the video recording of the third day’s session, Outcome Based Education – A Canadian Experience by Dr Thomas Varghese.
Day 4 Technical Session:
Topic: Underlying Threads of OBE Generative AI in Teaching by Dr Suresh Namboothiri.
Dr Suresh Namboothiri was the resource person for the third day of the one-week Faculty Development Programme with the topic Underlying Threads of OBE, Generative AI in Teaching.

Outcome-Based Education (OBE) emphasizes the achievement of specific learning outcomes, fostering a learner-centred approach that prioritizes the needs and goals of students. By focusing on what learners should be able to accomplish by the end of a course, OBE aligns educational practices with real-world applications, ensuring that students are well-equipped to navigate future challenges.
The integration of Generative AI in teaching presents a transformative opportunity to enhance the OBE framework. Generative AI tools can facilitate personalized learning experiences by adapting content to meet individual student needs, enabling educators to provide tailored support and resources. This synergy between OBE and Generative AI not only enhances student engagement but also promotes deeper understanding and mastery of subject matter.
Moreover, the use of Generative AI encourages innovative assessment methods, allowing educators to evaluate student progress through diverse and dynamic means. By harnessing these technologies, educators can track learning outcomes more effectively and provide timely feedback, ultimately leading to improved educational experiences and outcomes. Together, OBE and Generative AI create a powerful framework for shaping the future of education.
The third task in the form of Multiple Choice Questions was assigned to participants after the fourth day’s session, Underlying Threads of OBE, Generative AI in Teaching by Dr Suresh Namboothiri.
Click to watch the video recording of the fourth day’s session, Underlying Threads of OBE, Generative AI in Teaching by Dr Suresh Namboothiri.
Day 5 Technical Session:
Topic: Generative AI in Research by Dr Suresh Namboothiri.
Dr Suresh Namboothiri continued to be the resource person on the fifth day of the National Level Online Faculty Development Programme with the topic Generative AI in Research.

Generative AI refers to a class of artificial intelligence models capable of creating new content, such as text, images, and data, by learning patterns from existing datasets. This transformative technology leverages algorithms and neural networks, enabling researchers to automate tasks and generate novel insights. With its ability to mimic human creativity and reasoning, generative AI is revolutionizing various fields, including natural language processing, computer vision, and drug discovery.
In the realm of academic research, generative AI facilitates enhanced data analysis, enabling researchers to identify patterns and correlations that may not be readily apparent. By synthesizing information from vast datasets, these models assist in hypothesis generation, leading to more robust and innovative research outcomes. This capability not only streamlines the research process but also fosters interdisciplinary collaboration by providing a common framework for data interpretation.
Moreover, generative AI plays a critical role in improving reproducibility and transparency in research. By documenting and sharing the algorithms used in generative processes, researchers can ensure that findings are verifiable and reproducible. This fosters trust within the scientific community, encouraging the adoption of AI tools in research methodologies.
As generative AI continues to evolve, its applications are expected to expand further, paving the way for breakthroughs in diverse fields. From accelerating drug development to enhancing creative writing and artistic expression, the potential of generative AI in research is vast and promising, opening new avenues for exploration and innovation.
The fourth task in the form of Multiple Choice Questions was assigned to participants after the fifth day’s session, Generative AI in Research by Dr Suresh Namboothiri.
Click to watch the video recording of the fifth day’s session Generative AI in Research by Dr Suresh Namboothiri.
Day 6 Technical Session:
Topics: Mapping of Outcomes by Dr Mendus Jacob & Outcome Based Research by Dr Kamal Shah.
Mapping of Outcomes: Dr Mendus Jacob
Mapping of outcomes is a strategic process used in education and training to align learning objectives with assessment methods and intended results. It involves identifying the desired outcomes of a program or course and establishing clear connections between these outcomes and the instructional activities designed to achieve them. This systematic approach ensures that both educators and learners understand the goals and can assess progress effectively.
The primary purpose of outcome mapping is to enhance the quality and relevance of educational programs. By clearly defining what students should know and be able to do by the end of a course, institutions can create targeted teaching strategies and assessment tools. This alignment not only improves teaching effectiveness but also fosters student engagement and accountability.
Furthermore, mapping outcomes supports continuous improvement within educational frameworks. By regularly reviewing and adjusting outcomes based on feedback and assessment results, institutions can ensure that their programs remain effective and responsive to the needs of students and the job market. This iterative process promotes a culture of excellence and accountability in education.
In summary, outcome mapping is essential for aligning educational objectives with assessments and instructional strategies. It enhances program quality, supports student success, and fosters continuous improvement, making it a vital component of modern educational practices.

Outcome Based Research: Dr Kamal Shah
Outcome-Based Research (OBR) is an innovative approach that emphasizes the tangible results of research efforts rather than solely focusing on the processes involved. This methodology prioritizes the impacts and implications of research findings, aligning them with the needs of stakeholders, including policymakers, practitioners, and communities. By concentrating on specific outcomes, researchers can ensure their work addresses real-world challenges and contribute to meaningful advancements in their fields.
In OBR, the design and execution of research projects are guided by clearly defined goals. This framework encourages researchers to set measurable objectives from the outset, facilitating the assessment of outcomes at various stages of the research process. By employing rigorous evaluation methods, OBR provides a structured means of determining the effectiveness of interventions and strategies, thereby enhancing accountability and transparency in research.
Furthermore, OBR promotes collaboration among various stakeholders, fostering partnerships that enrich the research process. Engaging stakeholders from the beginning ensures that the research is relevant and addresses pressing needs, ultimately enhancing the likelihood of successful implementation and impact. As a result, OBR not only advances academic knowledge but also contributes to the betterment of society by translating research findings into actionable solutions.
The fifth and sixth tasks, Formulation of Assessment Questions with respect to a Course Outcome and Finding the Mapping Strength and CO Computation Prototype Model, and the seventh task in the form of Multiple Choice Questions were assigned to the participants after the sixth day’s session.
Click to watch the video recording of the sixth day’s sessions, Mapping of Outcomes by Dr Mendus Jacob and Outcome Based Research by Dr Kamal Shah.
Day 7 Technical Session:
Topic: Attainment Calculation and Various Analytical Reports and, Useful ICT Tools and OBE for Accreditation by Dr Mendus Jacob.

Attainment calculation:
Attainment calculation is a critical process that evaluates the performance and achievement levels of students or educational programs. It involves assessing various metrics to determine how well learners meet established learning objectives and outcomes. By systematically measuring attainment, institutions can gain insights into educational effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Various analytical reports stem from attainment calculations, providing valuable data for stakeholders. These reports typically include performance trends, demographic analyses, and comparisons across different cohorts or programs. Such comprehensive evaluations help educators understand the effectiveness of their teaching strategies and curriculum design.
Additionally, analytical reports serve as essential tools for decision-making within educational institutions. They offer actionable insights that can inform policy adjustments, resource allocation, and strategic planning. By leveraging data-driven findings, institutions can enhance their overall educational quality and foster student success.
In summary, attainment calculation and its associated analytical reports are vital components of effective educational assessment. They empower institutions to track progress, identify strengths and weaknesses, and implement targeted improvements that support student learning outcomes.
Useful ICT Tools:
After the session, Dr Mendus gave a demonstration of QnSmart i, the Question Bank and Question Paper Generation Tool with an in-built Bloom’s Taxonomy, focusing on OBE, Quality Control, Best Practices, and Cost Efficiency for Higher Education Institutions and Universities, deQ OBE, an innovative tool that aids HEIs in managing Outcome Based Education comprehensively, from defining POs, PSOs, and COs to calculating attainment and generating reports for accreditation agencies, and Questionpaper.ai, an AI-assisted academic platform that generates question papers, course outcomes, syllabi, or assignment topics within minutes by simply entering the syllabus or topic.
OBE for Accreditation:
Outcomes-Based Education (OBE) is a student-centred approach focusing on achieving specific learning outcomes. It emphasizes the skills and competencies students should acquire by the end of their educational experience. By defining clear, measurable outcomes, OBE facilitates a structured learning environment where both educators and students can track progress and achievement.
In the context of accreditation, OBE provides a robust framework for evaluating educational programs. Accreditation bodies look for evidence that institutions effectively promote student learning and development. By aligning curricula with clearly defined outcomes, institutions can demonstrate their commitment to delivering quality education that meets industry standards and stakeholder expectations.
Moreover, OBE supports continuous improvement in educational practices. It encourages institutions to regularly assess and refine their programs based on student performance and feedback. This cycle of evaluation and enhancement not only strengthens the case for accreditation and fosters a culture of excellence and accountability within educational institutions.
The eighth and final task, Submit an Article on Innovative Practices in Teaching and Learning for Publishing Online was assigned to the participants at the end of the final day’s session.
Click to watch the video recording of the seventh day’s session, Attainment Calculation and Various Analytical Reports, Useful ICT Tools and OBE for Accreditation by Dr Mendus Jacob
Join us for FREE to get instant email updates!

The Internal Quality Assurance Cell (IQAC), in collaboration with the […]

A one-day workshop on Demystifying Outcome-Based Education (OBE) was successfully […]

As part of Mar Athanasius College of Engineering’s continuous pursuit […]

A one-day workshop on Smart Assessments with the OBE Approach […]

A one-day national-level workshop on Demystifying Outcome-Based Education (OBE) was […]

The Faculty Development Programme on Outcome Based Education (OBE) was […]

St. John Group of Institutions, under the Aldel Education Trust, […]

MES KEVEEYAM College, Valanchery, Malappuram, successfully hosted a One-Day National […]

As part of Parul University’s continued commitment to enhancing academic […]
Leave A Comment